
The regulation of Fintech goods and services is handled by a number of different regulatory bodies. Various regulatory organizations oversee various Fintech services and products. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC), China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), and China Securities Regulatory Commission are the key institutions in charge of enforcing regulations (CSRC) and structuring fintech regulations in China.
Customer Lending

The General Rules of Loans, the Administrative Measures for Pilot Consumer Finance Companies (the Consumer Finance Measures), and the Commercial Bank Law all control consumer lending, making it a regulated industry. The CBIRC has published the Trial Rules for Rating Consumer Finance Companies’ Supervision.
The General Rules of Loans provide that lenders must be registered with the State Administration for Market Regulation, be approved by the PBOC to hold financial institute legal person permission, or have a financial institute operating permit granted by the PBOC, in order to conduct lending operations.
The Consumer Finance Measures set forth rules for how consumer finance businesses—often referred to as non-bank financial institutions—operate. These businesses do not accept public deposits but instead, lend money to residents of China for consumption—apart from home and vehicle purchases—under the small sum and dispersion principle. The CBIRC must provide approval to consumer finance firms.
Consumer finance firms will get rating results from CBIRC in accordance with the Trial Rules for Supervision Rating for Consumer Finance Companies. According to the outcomes of their ratings, these firms will be subject to various regulatory procedures.
Crowdfunding
Equity-based crowdfunding is described by the Guideline Opinion on Promoting the Healthy Development of Internet Finance as public equity financing in modest sums using an online platform. The Opinion stipulates that equity crowdfunding must be carried out through a platform operated by an agency, such as a website or other digital media, and that the CSRC would act as the industry’s regulating body.
The formation of private equity funds or the public issuance of securities through crowdfunding is prohibited under the CSRC’s 2016 action plan for risk control of equity-based crowdfunding. However, in fact, operators frequently utilize crowdfunding to obtain money in an unauthorized manner, which has prompted a wave of government crackdowns. As a result of its growing negative effects, regulators do not favor crowdfunding.
Invoice Trading & Financial Institutions
oney orders, promissory notes, and checks are included in the three kinds of negotiable instruments covered under the 2004-issued Negotiable Instruments Law. It lays forth guidelines for the three negotiable instruments’ transfer, endorsement, acceptance, and payment.
In China, receivables can be utilized to finance projects. Although the Rule on Promotion of Small and Medium Enterprises specifically encourages such funding, there is presently no law or regulation on the subject. Account receivables are registered on an internet platform run by the PBOC’s Credit Reference Center in order to acquire financing from banks, approved non-bank financial institutions, or factoring firms.
Open Banking & China Securities Regulatory Commission
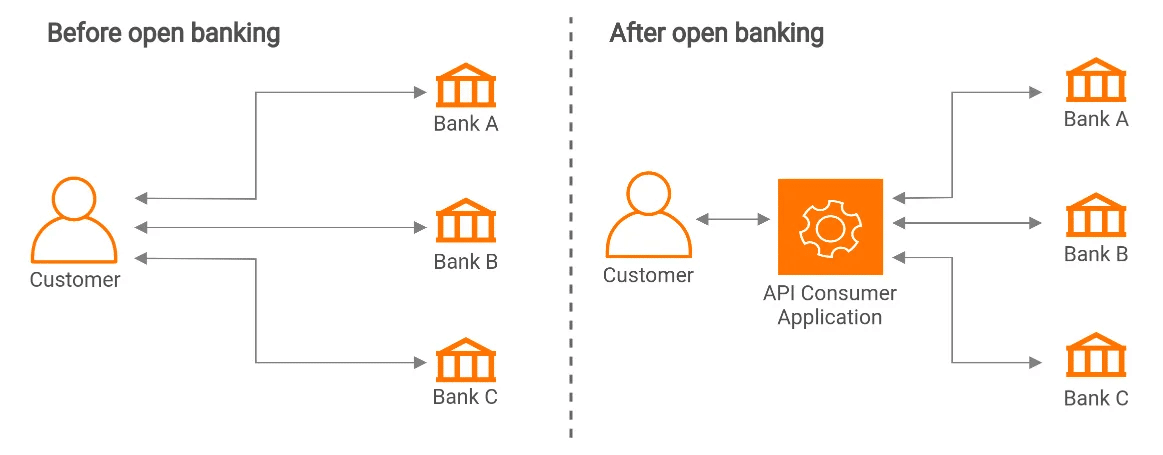
At the moment, China has no such rules or legislation. The financial industry standard for the application programming interface secure management specification for commercial banks was released by the PBOC on February 13th, 2020.
In addition to other security technology and standards, the standard specifies the kind and security level of the application programming interface (API) used by commercial banks as well as the security design, deployment, integration, operation, and maintenance processes.
Additionally, China will continue to support the modernization of digital channels (such as APIs) and the establishment of “complete financial service platforms,” according to the Fintech Plan (2022-2025) released by the PBOC. The Fintech Plan also specifies that a variety of technologies would be employed to investigate safe data exchange, as well as mechanisms for determining ownership of data.
The objective is to achieve systematic data exchange among institutions, regions, and industries. As a result, it is anticipated that China will soon introduce pilot programs to encourage financial institutions to share data.
Insurance Products & Fintech Companies
Internet insurance providers must abide by the CBIRC’s Measures for the Regulation of Internet Insurance Business in addition to the normal insurance laws and regulations. To do business, insurance brokers and corporations need a CBIRC license. They are allowed to carry out online insurance business using either their own platforms or those of thirds.
The Notice on Further Regulating Internet-based Life Insurance Business of Insurance Firms, which outlines requirements and limitations for insurance companies to conduct life insurance business online, was published by the CBIRC in October 2021.
Credit References
The main rules governing credit references and credit information services are found in the Administrative Regulations on the Credit Reporting Industry. While the providers of personal credit information services are subject to prior permission from the PBOC and tougher qualification standards, the providers of corporate credit information services are subject to filing requirements with the PBOC.
In 2018, the PBOC granted Baihang Credit Co. Ltd., a newly formed corporation with eight firms and the National Internet Finance Association as its owners, its first personal credit rating business license. The PBOC granted Pudao Credit Co. Ltd., a joint venture with owners from a significant Beijing municipal government-controlled financial group and leading private enterprises, its second personal credit rating business license in December 2020.
Payment Services
Under the Administrative Measures for the Payment Services Provided by Non-financial Institutions, the PBOC regulates payment services offered by non-financial institutions (payment service providers) in China. Any of the following transfer services offered by non-financial companies as the middlemen between the payer and the payee are referred to as “payment services”:
Acceptance of payments made with a bank card and any further payment services that the PBOC deems necessary
issuing prepaid cards
Online Payments

To offer payment services in China, a supplier of payment services must get a PBOC-issued payment service license by central bank. In addition to the payment license granted by the PBOC, payment service providers will need to get a license from the foreign exchange authorities (i.e., the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE)) for cross-border payments.
The PBOC’s Measures for the Deposit of Pending Payments of Clients of Non-bank Payment Institutions, published in January 2021, mandate that non-financial payment institutions deposit client reserve monies in accounts with the PBOC or approved commercial banks in order to safeguard the funds.
In January 2021, the PBOC released a draught Regulation on Non-banking Payment Agencies to purify regulatory environment. The operation of prepaid accounts and the processing of payment transactions are the two new categories for payment services included by this draught rule.
It lays forth guidelines for the establishment, granting of licenses, management, and oversight of non-banking payment providers in China. The proposed legislation includes safeguards for safeguarding personal data and controlling monopolies. The proposed regulation is currently being worked on as of June 2022.
Conclusion
The formulation of “Measures for the Administration of Cross-border Payment Services” has been placed on the agenda to further regulate cross-border payment services, according to the legislation plan released by the PBOC on April 17, 2020. However, as of June 2022, these proposed policies have not undergone any more development.



